Plant modeling and AI
We focus on the generation of synthetic ground truth data (images or point clouds) using virtual plant models, and on novel analysis techniques for 3D and 3D+time data.
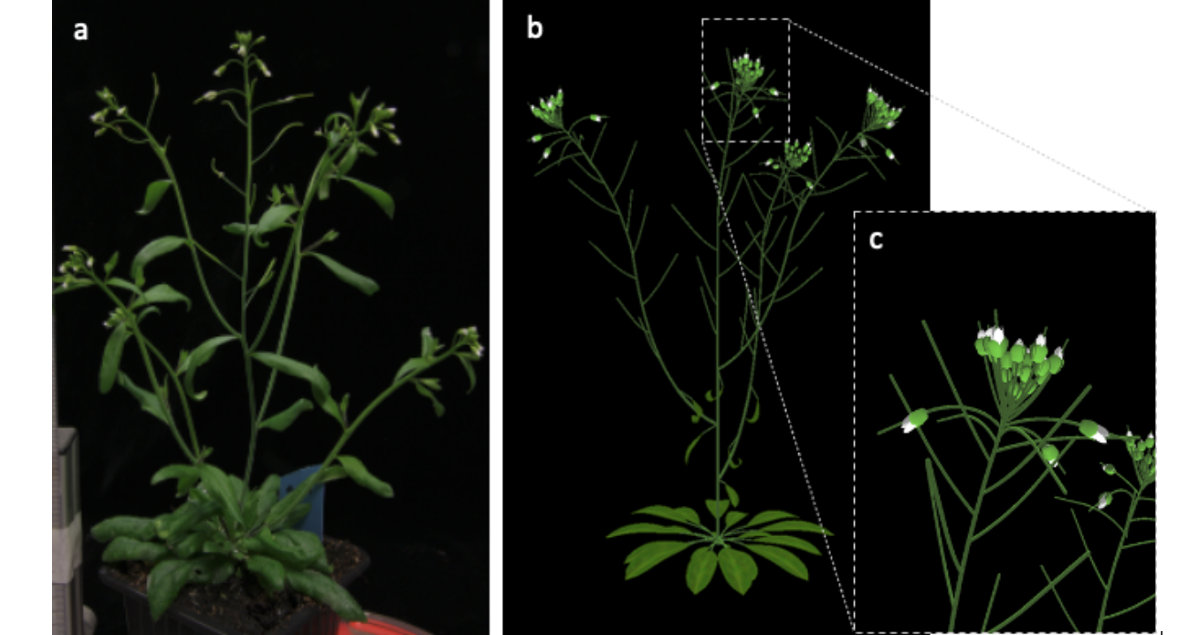

The work on the plant models has resulted in approved models for Arabidopsis thaliana and tomato plants. The model of A. thaliana was successfully used to train neural networks for the semantic segmentation of images of real plants and to produce high-quality point clouds for subsequent machine learning and analysis tasks.
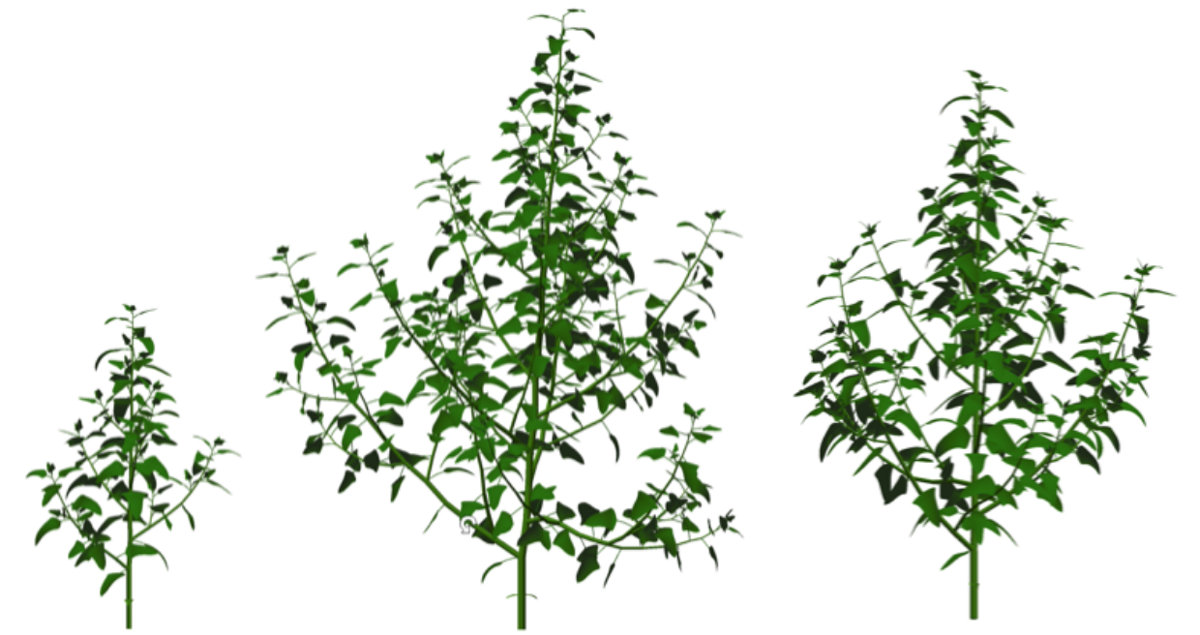

This motivates the work to go further into the realistic rendering of plants and improve the physical coherence of the generated 3D plants. Existing state-of-the-art models, including ours, do not correctly detect and handle intersecting organs, for example. This problem is currently investigated together with other key issues related to photo-realistic rendering of plants.
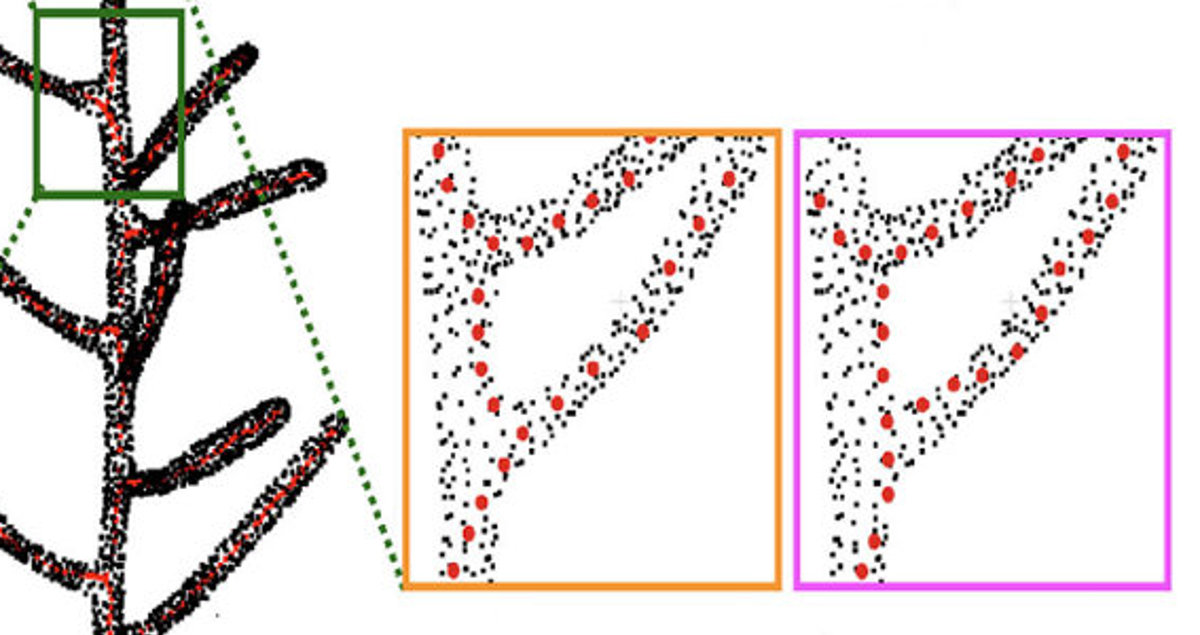
The challenge remains to robustly segment 3D plant data into its constituent organs can be tackled using several methods, from geometric methods to machine learning methods that use 2D image segmentation or 3D point cloud segmentation. An additional challenge is the precise extraction of the plant's skeleton from a 3D representation.
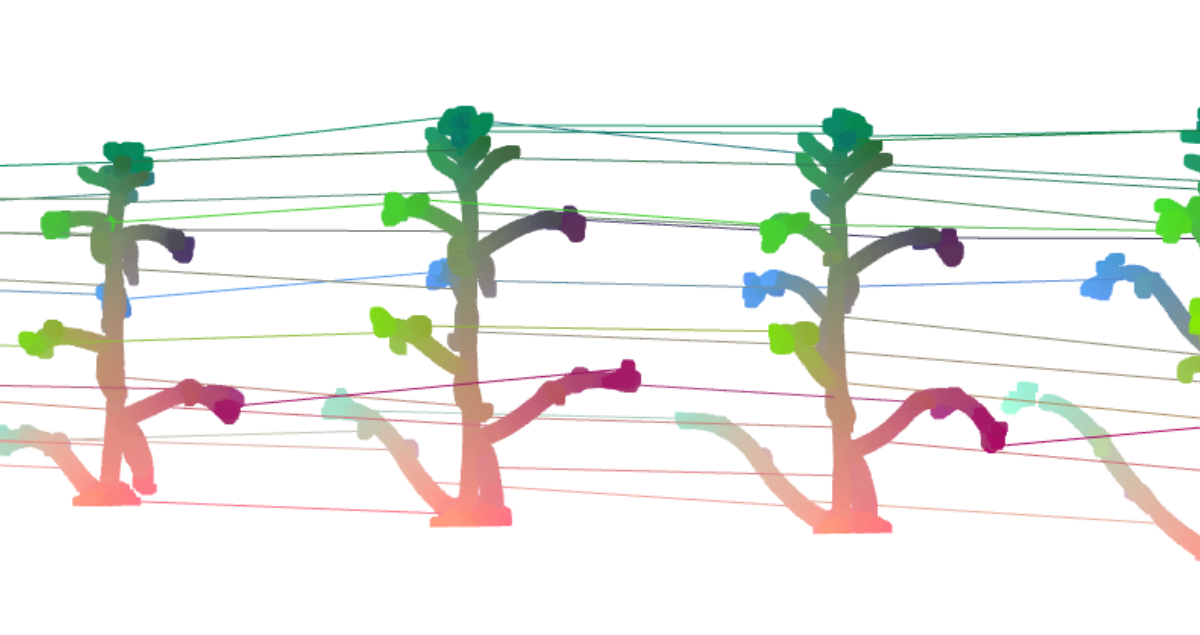
Tracking the plant growth over time raises the issue on the space-time registration of the collected 3D data. The combination of plant models and machine learning may help us predict the plant's shape ahead of time.